The Rise of Virtual Reality Simulators – Guide

Thanks to the advancements in technology, literally everything can be simulated in VR. I remember learning how to drive in a racing simulator equipped with VR headsets before getting my hands on a real-life car. There was exactly nothing new to learn, and I seamlessly transitioned my simulator driving skills to driving a real car.
Nothing is better learned than from what is practiced by doing, and virtual reality simulators allow us to achieve just that. Not everything can be easily and feasibly replicated to enable an individual to train as many times as they want. Virtual reality simulators, however, remove this restriction. In my case, a racing simulator saved me from fuel costs, real car accidents, and training fees.
That is why, despite their higher initial costs for setup, many businesses now view them as more budget-friendly options in the long run. From being looked down upon to being revered in the industrial market, let’s look at the rise of virtual reality simulators!
What Is A VR Simulator?

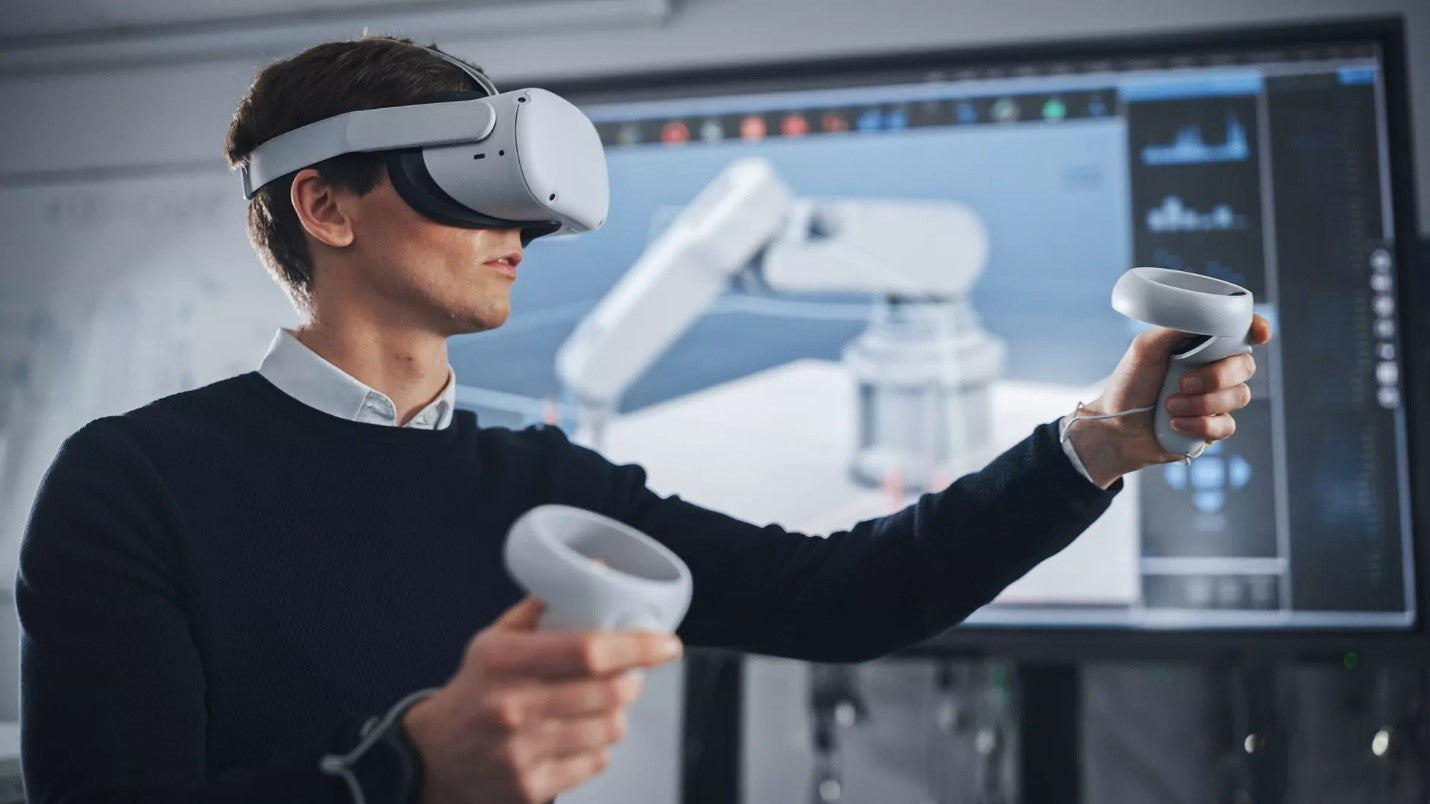
A VR simulator (or virtual reality simulator) is an advanced, high-tech system that enables a user to experience a real-world situation within a completely 3D digital environment. With specialized equipment like virtual reality headsets, motion detection devices, and even gloves with haptics, it creates a 3D virtual world that responds to your actions like one would experience in reality.
You look around, walk, grab objects, or even drive, and the system reacts instantly. The headset is the main piece of gear. It shows you the virtual world in 3D, while built-in speakers create sounds that match the environment around you. Motion tracking watches your body and adjusts the experience in real time.
All of this works together in real-time to create an immersive experience that feels incredibly lifelike.
A Bit of a Background

So where did all this come from? The answer might surprise you because while it feels new and fresh, virtual reality has been around for decades. The first official virtual reality headset was created by computer scientist Ivan Sutherland in 1968. It was a heavy mechanical device that had to be suspended from the ceiling to be operated, so not exactly what you’d call portable. What’s more is that it even had a funny name: The Sword of Damocles. Yet it was the first step that marked the beginning of the rise of virtual reality simulators.
In the 1970s and 80s, VR simulators started appearing in the military and aviation sectors, where pilots and soldiers practiced in safe, controlled virtual environments. As such, the U.S. Air Force used them to train pilots without ever leaving the ground. One of the key pioneers during this time was Tom Furness, who worked on advanced flight simulators for the U.S. Air Force. Although a lot of that work stayed classified, it helped shape the path of VR development.
In the 1990s, as computers improved, so did VR. Systems became more interactive with better graphics. But it was the 2010s that truly changed everything when the Oculus Rift came along. It practically pushed the rise of virtual reality simulators into the mainstream. Since then, virtual reality simulators have continued to transform industries from gaming and healthcare to education and engineering.
Modern-Day Applications of VR Simulators
Gaming and Entertainment

Gaming is where many people first get introduced to VR, and it’s no surprise why. The experience feels like stepping into another world where you’re no longer just playing a game, you’re in it. This is where the rise of virtual reality simulators has truly taken off.
Take racing simulators, for example. With a VR headset and a motion-enabled chair, you can sit in the driver’s seat of a Formula 1 car, feeling every turn and bump. Systems like Wantec VR and TracksVR offer realistic driving physics, detailed tracks, and even steering wheels that push back when you hit a curb.
Then there’s VR flight simulation. Programs like Microsoft Flight Simulator VR recreate the entire cockpit of real planes — from instrument panels to weather changes — letting gamers or even flight trainees soar through the skies without leaving the ground.
On platforms like SteamVR, popular games such as VRChat, No Man’s Sky VR, and Elite Dangerous open up massive worlds to explore. And with wireless devices like the Meta Quest 2, players enjoy freedom of movement with hand tracking and a growing game library. Add in motion chairs like the Roto VR or Yaw2, and it’s no longer just playing, it’s experiencing.
Medical and Healthcare

In addition to gaming and entertainment, the medical field has also seen huge benefits from the rise of virtual reality simulators. For surgeries or those who play a critical role in healthcare, virtual reality creates a controlled environment where they can learn and practice without fear of injuring or negatively impacting a live patient.
For example, VR surgical simulators now let surgeons to perform surgery in a 3D world without real-world consequences for medical students and aspiring surgeons. They can understand how to hold instruments, follow surgical steps and even cut or sew thanks to haptic feedback. Simulation programs like Osso VR and Touch Surgery offer detailed 3D visuals that accurately replicate what's inside a human body.
Emergency response teams also use VR to train for high-stress situations. Whether it’s a road accident or a natural disaster, responders can learn how to stay calm, make decisions quickly, and treat injuries — all inside a virtual world.
And it’s not just about training. Virtual reality is also being used in therapy. Patients with anxiety, PTSD, or chronic pain are now using VR-based treatments that help them relax or rewire how their brain handles stress. Studies show VR therapy can even reduce pain levels without needing medication.
Professional and Technical Training

In many industries, training people can be expensive, risky, or just hard to repeat. That’s where virtual reality simulators shine. VR now helps professionals build skills in a safe and realistic environment without ever needing actual machines, tools, or dangerous setups.
In construction, for example, VR simulators teach workers how to handle heavy machinery, follow safety rules, and read site layouts. Using dedicated simulator programs like STRIVR allows them to create realistic building scenarios and hazard detection training programs that can help prevent potential accidents before they happen in real life.
Manufacturing, oil and gas, and engineering fields are also using VR to simulate risky environments. Systems like Honeywell VR train employees on pipeline controls, machinery maintenance, and chemical handling — all without the danger of real exposure.
There are also VR firefighting simulators. These help firefighters prepare for smoke-filled buildings, spreading flames, and life-threatening decisions — all through virtual reality, using real-time fire behavior models. Even military forces now rely on VR to prepare soldiers for battlefield situations, drone operations, and high-pressure combat scenarios.
Automotive and Aviation Training

Learning how to drive or fly a plane isn’t something you want to get wrong in any of your attempts — that's why VR simulators are so popular in these sectors. These industries have significantly contributed to the rise of virtual reality simulators in other sectors as well, simply by showcasing how much racers and pilots benefited by training in simulation.
For instance, driving schools and pilot training centers have driving simulators. Before hitting the actual road, students can perfect their skills in a controlled, virtual setting. These simulators mimic everything from traffic and weather to braking, turning, and reacting to road hazards. SimXperience and Gran Turismo VR are two such simulation software that are helping drivers build confidence and skills without the risk of accidents or extra costs.
VR is changing how we train in aviation. For example, Boeing and Airbus use VR for their flight simulators. These include cockpits with actual controls, voice-command checklists, and practice for emergency response. They allow pilots to learn how to fly in various weather conditions, different time zones, and emergencies, without ever leaving the ground.
While this is a massive time and money saver, it also provides a level of experience that was previously unimaginable. For example, not long ago, there was no way to practically learn how to fly without learning at least some components of the training while actually flying; however, with VR, students can repeat and learn in the safest and most practical environments until they have fulfilled their mandatory requirements.
Is VR Simulation the Future?

Looking at how quickly it’s being adopted across industries, from gaming and healthcare to aviation and emergency training, it’s clear that the rise of virtual reality simulators is just the beginning. As the technology becomes more affordable and even more immersive, VR is set to become a standard tool for learning, testing, and exploring. The future isn’t just virtual, it’s already here!